Contents:
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Installation
- 3. Setup and Configuration
- 4. Enable Web Access
- 5. Verify that Cellular Access is Available
- 6. Setting Up the Firewall/IP Tables (Optional)
1. Introduction
This Quick Start Guide provides a basic overview of the procedure for installing and setting up WTI’s Cellular Modem option on WTI Devices.
- Although both the Command Line Interface (CLI) and Web Browser Interface can be used to adjust cellular parameters once cellular communication has been set up, the CLI includes vital configuration functions that are not present in the Web Browser Interface. For this reason, the CLI is used when setting up the Cellular Modem Option.
- Prior to setting up the Cellular Modem Option, it is recommended to install and configure your WTI Device as described in the Hardware Guide.
- When accessing the WTI Device’s Command Mode, please refer to the WTI User’s guide for further instructions.
https://www.wti.com/blogs/knowledge-base/basic-info-for-setting-up-the-cell-interface
2. Installation
In order to communicate with your WTI Device via the Cellular Modem Option, you will first need to purchase a cellular plan.
When choosing a cellular plan, WTI recommends that the plan should provide the following:
- A Static IP Address is recommended, but not required. If you need to use a Dynamic IP Address, then a DDNS provider will be required.
- A VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- An IOT/M2M Data Plan
- An APN (Access Point Name) to establish an active PPP session.
- A 2FF SIM Card
- Mobile terminated data
- When configuring your network, SSH port 22 and HTTPS port 443 should both be Open.
2.1. Attach the Cellular Antennae
Attach the two Cellular Antennae, (included with the unit,) to the two threaded connectors on the WTI Device's face plate.
2.2. Installing the SIM Card
Once you have purchased a cellular plan, the next step is to install the SIM card, (provided with your cellular plan,) in your WTI Device. To install the mini SIM card, proceed as follows:
Notes:
- The SIM Card slot is designed to accept a form factor 2FF SIM Card .
- Prior to installing the SIM Card, make certain that the WTI Device is powered Off.
- If rack brackets have been installed on the WTI device, it will be necessary to remove the rack brackets in order to expose the SIM Card cover panel.
- Remove the SIM Card cover panel on the left hand side of the WTI unit, located adjacent to the cellular antenna as shown in Figure 2.1 below. Note that the panel is held in place by a small Phillips Head screw.
- Carefully slide the SIM card into the SIM Card Slot with the keyed/notched corner of the card facing towards the unit’s faceplate (see diagram on cover plate.) Make certain the SIM Card is firmly seated, but do not apply excess pressure that might damage the card.
- Replace the panel that covers the SIM Card Slot, reinstall the retaining screw and restore power to the WTI Device.
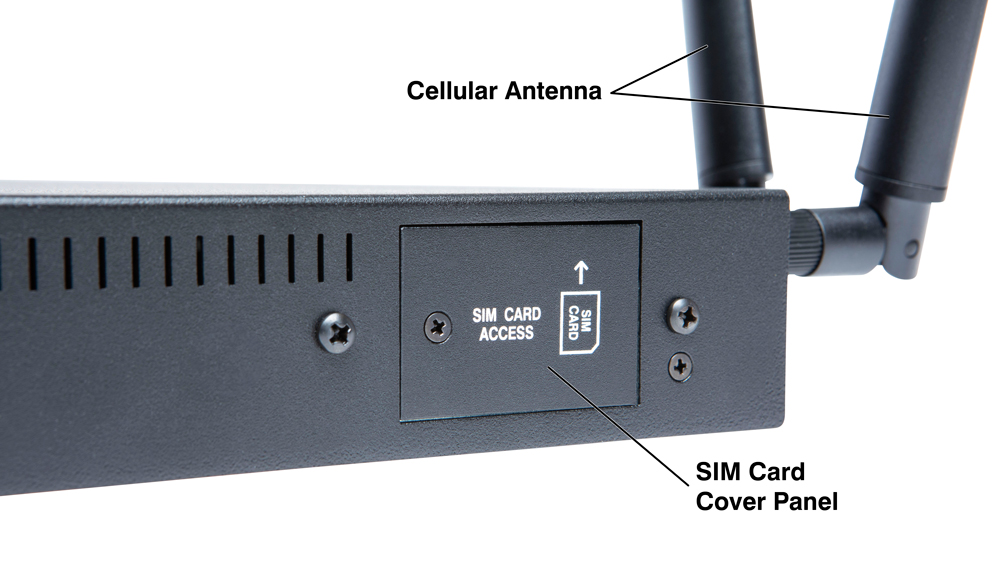

Figure 2.1: The SIM Card Cover Panel
3. Setup and Configuration
After the cellular antennae and SIM Card have been installed, the next steps are to configure the SIM Card and define the Static Route.
Notes:
- Although both the Command Line Interface (CLI) and Web Browser Interface can be used to adjust cellular parameters once cellular communication has been set up, the CLI includes vital configuration functions that are not present in the Web Browser Interface. For this reason, the CLI is used when setting up the Cellular Modem Option.
- Prior to setting up the Cellular Modem Option, it is recommended to install and configure your WTI Device as described in the Hardware Guide.
- When accessing the WTI Device’s Command Mode, please refer to the WTI User’s guide and the link below for further instructions.
https://www.wti.com/blogs/knowledge-base/basic-info-for-setting-up-the-cell-interface
3.1. Configuring the SIM Card
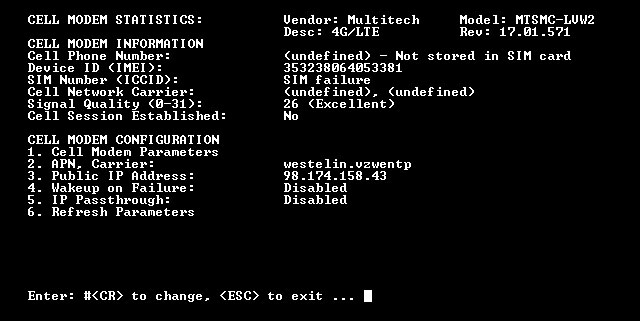
After installing the SIM Card, use the /cell command to configure the SIM Card as described below:
- Access the Text Interface Command Mode for the WTI Device via Console Port or Network Port.
- When the command prompt appears, type /cell and press [Enter] to display the Cell Modem Statistics menu as shown in Figure 3.1 above.
- At the Cell Modem Statistics menu, select “APN, Carrier.”
- At the Access Point Name configuration menu, use the Access Point Name (APN) option to key in the APN, (supplied with your cellular plan,) and press [Enter]. Use the Carrier option to select the service provider (carrier) that the REM will use. The Cellular Modem Option will be automatically configured, based on the information on the SIM Card.
- The configuration procedure may take several minutes. When configuration is complete, Cell Modem Statistics menu will be redisplayed, indicating that configuration was successful.
3.2. Defining the Static Route
After the SIM Card has been installed and configured, the next step is to define the Static Route.
Note: The Static Route is only required if the Cell Modem Port is not defined as the default gateway.
3.2.1. Defining Static Route when the Default Gateway Address is Known
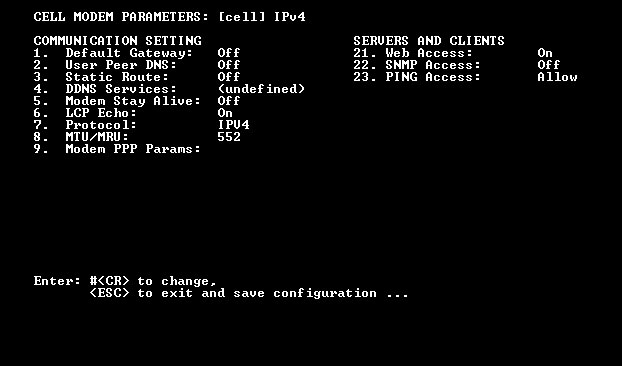
Figure 3.2: The Cell Modem Parameters Menu
If you already know the default gateway address for your cellular network, then proceed as follows. If you don't know the default gateway address, please proceed to Section 3.2.2.
- Type /p modem and press [Enter] to display the Cell Modem Parameters menu as shown in Figure 3.2 above..
- When the Cell Modem Parameters menu is displayed, select Static Route to display the Static Route submenu. When the Static Route submenu is displayed, key in a number for the first vacant Static Route definition line and press [Enter].
- Define the Static Route using the following format:
- Press [Esc] once to exit the Static Route menu, then press [Esc] again to exit the Cell Modem Parameters menu and save the newly defined Static Route. Note that it may require several minutes for the Cell Modem to save newly defined parameters.
- Perform the verification procedure described in Section 5 to make certain that cellular access has been properly enabled.
3.2.2. Defining Static Route when the Default Gateway Address is Unknown

Figure 3.3: The Network Parameters Menu
If you don't know the default gateway address used by the cellular network, then you will need to use the WTI Device's /bash command to display the default gateway address as described above:
- If you are communicating via local network and do not require the default gateway address, log into the WTI Device via serial port, USB or network (if your network is on the same network and doesn’t require the default gateway.)
- Temporarily Disable Default Gateway for the Network Port: When the command prompt appears, type /N and press [Enter] to display the Network Parameters menu as shown in Figure 3.3 below.
- At the Network Parameters menu, select Gateway Address. The Gateway Address submenu will be displayed. Record the currently defined Gateway Address.
- At the Gateway Address submenu, press the [Space] bar and then press [Enter]. This will delete the currently defined Gateway Address, disabling the Default Gateway at the Network Port.
- Press [Esc] twice to exit the Network Parameters menu and save changed parameters.
- Enable the Default Gateway for the Cell Modem Port: At the Text Interface command prompt, type /p modem and then press [Enter] to display the Cell Modem Parameters menu.
- When the Cell Modem Parameters menu is displayed, select Default Gateway. Use the resulting menu to enable the Default Gateway for the Cell Modem Port.
- Press [Esc] twice to exit the Default Gateway menu and save newly defined parameters.
Note: It may require several minutes for the Cell Modem to save the newly defined Default Gateway status.
- Display the IP Address for the Cell Modem Port:
- At the WTI Device command prompt, type /cell and press [Enter] to display the Cell Modem Statistics menu.
- When the Cell Modem Statistics menu is displayed, write down the IP Address for the Cell Modem Port (listed under the Cell Connection Information heading.)
- Press [Esc] to exit from the Cell Modem Statistics menu.
- Establish an SSH connection to the WTI Device via the cellular network.
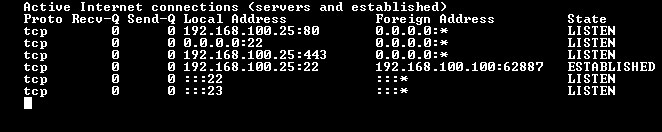
Figure 3.4: The Active Internet Connections Screen
- Display the Gateway Address: At the WTI Device command prompt, type /bash netstat -nat and press [Enter] to display the Active Internet Connections screen, shown in Figure 3.4 above. Note that it may take several minutes for the unit to respond.
- The Cell Modem Port IP Address with be displayed in the "Foreign Address" column.
- The "State" column for the Cell Modem Port IP address will read “Established.”
- Note the Gateway Address (Local Address,) that corresponds with the Cell Modem Port IP address (Foreign Address.)
- To exit from the Active Internet Connections menu, press [Enter].
- Define the Static Route: At the WTI Device command prompt, type /p modem and press [Enter] to display the Cell Modem Parameters menu as shown in Figure 3.1.
- When the Cell Modem Parameters menu is displayed, select Static Route to access the Static Route submenu. When the Static Route submenu is displayed, key in a number for the first vacant Static Route definition line and press [Enter].
- At the Static Route menu, refer to the Cell Modem Port Address (Foreign Address) and Gateway Address (Local Address) that were determined above. Enter a route command using the following format:
- Press [Enter] to select the newly defined Static Route, then press [Esc] twice to save the Static Route definition and exit the Static Route menu. Note that it will require several minutes for newly defined parameters to be saved.
- For more information, please refer to the following example:
Static Route Definition Example:
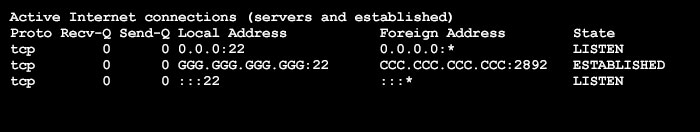
Figure 3.5: Static Route Definition Example
Assume that the address for the Cell Modem Port address (Foreign Address) is CCC.CCC.CCC.CCC and the netstat function returns the Active Internet Connections screen shown in Figure 3.5 above. In this example, the Gateway Address (Local Address) would be GGG.GGG.GGG.GGG. Therefore, the static route would be defined as follows:
route add GGG.GGG.GGG.GGG gw CCC.CCC.CCC.CCC
- Disable the Default Gateway for the Cell Modem Port:
- At the WTI Device command prompt, type /p modem and press [Enter] to display the Cell Modem Parameters menu.
- When the Cell Modem Parameters menu is displayed, access the Default Gateway submenu and disable the Default Gateway for the Cell Modem Port.
- Press [Esc] twice to exit from the Cell Modem Parameters and save the newly defined Default Gateway Status.
Note: It may require several minutes for the Cell Modem to save the newly defined parameters.
- Re-Enable the Default Gateway for the Network Port: When the command prompt appears, type /N and press [Enter] to display the Network Parameters menu.
- At the Network Parameters menu, select Gateway Address. The Gateway Address submenu will be displayed.
- At the Gateway Address submenu, key in the previous Gateway Address that you saved in Step 2 at the beginning of this section and then press [Enter].
- Press [Esc] twice to exit the Network Parameters menu and save changed parameters.
Note: It may require several minutes for the Cell Modem to save the newly defined parameters.
4. Enable Web Access
If you need to allow access to the WTI Device's web browser interface via cellular, you must enable Web Services via the Cell Modem Parameters menu.
- At the WTI Device command prompt, type /p modem and press [Enter] to display the Cell Modem Parameters menu (Figure 3.1).
- When the Cell Modem Parameters menu appears, select Web Access and then use the resulting submenu to enable Web access via cellular.
- Press [Esc] twice to exit from the Cell Modem Parameters menu and save the newly defined Web Services status.
Note: It may require several minutes for the Cell Modem to save the newly defined Web Access status.
5. Verify that Cellular Access is Available
After setting up Cellular Access, it is recommended to perform this procedure to verify that the procedure was completed successfully.
- If you are still connected to the WTI Device command mode, type /X and press [Enter] to disconnect from the unit.
- Verify Cellular Access to Text Interface (CLI).
- Create an SSH connection to the WTI Device via cell. When the login prompt is displayed, enter your username and password. When the command prompt appears, type /cell and press [Enter].
- If the Cell Modem Statistics screen appears, this indicates that cellular network access has been successfully enabled.
- If the Cell Modem Statistics screen fails to appear after several minutes, this probably means that there is an error in the definition of the Static Route. In this case, use the procedure described in Section 3 to display the Static Route definition. Carefully check the Static Route definition to make sure that the IP addresses were entered correctly and that there are no syntax errors.
- Verify Cellular Access to Web Browser Interface:
- Start your Web Browser, key the Cell Modem Port IP Address for the WTI Device into the browser’s address bar. When the login prompt is displayed, key in your username and password.
- If the WTI Device’s home page is displayed, this means that cellular access to the WTI Device has been successfully enabled.
- If the WTI Device’s home page is not displayed, this probably means that either Web Access has not been enabled as described in Section 4 or there is an error in the Static Route definition.
- Web Access Not Enabled: Make certain that web access has been enabled as described in Section 4.
- Static Route Error: Use the procedure described in Section 3 to display the Static Route definition. Carefully check the Static Route definition to make sure that the IP address were entered correctly and that there are no syntax errors.
6. Setting Up the Firewall/IP Tables (Optional)
If you wish to restrict access to the WTI Device via cellular, you must define a firewall. The IP Tables menu is used to define a firewall which determines which IP addresses will be allowed to access the WTI Device via cellular and which IP addresses will be denied. To define the firewall, proceed as follows:
- At the Text Interface command prompt, type /N and press [Enter] to display the Shared (eth0) Network Parameters menu.
- When the Network Parameters menu is displayed, select the IP Tables option.
- When the IP Tables menu is displayed, use Linux syntax to determine which IP address(es) will be allowed access and which IP address(es) will be denied. In most cases, the IP Tables should allow access to administrators and deny access to everybody else.
This completes the set-up procedure for the WTI Cellular Modem Option. For further information, please refer to the WTI User Guide and the following article in the WTI Knowledge Base:
https://www.wti.com/blogs/knowledge-base/basic-info-for-setting-up-the-cellinterface